 C[c] is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains widely used and influential. By design, C gives the programmer relatively direct access to the features of the typical CPU architecture, customized for the target instruction set.
C[c] is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains widely used and influential. By design, C gives the programmer relatively direct access to the features of the typical CPU architecture, customized for the target instruction set. The C Programming Language has often been cited as a model for technical writing, with reviewers describing it as having clear presentation and concise treatment.
The C Programming Language has often been cited as a model for technical writing, with reviewers describing it as having clear presentation and concise treatment.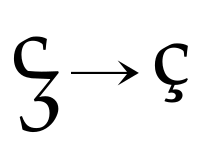 Ç or ç (C-cedilla) is a Latin script letter used in the Albanian, Azerbaijani, Manx, Tatar, Turkish, Turkmen, Kurdish, Kazakh, and Romance alphabets. Romance languages that use this letter include Catalan, French, Portuguese, and Occitan, as a variant of the letter C with a cedilla.
Ç or ç (C-cedilla) is a Latin script letter used in the Albanian, Azerbaijani, Manx, Tatar, Turkish, Turkmen, Kurdish, Kazakh, and Romance alphabets. Romance languages that use this letter include Catalan, French, Portuguese, and Occitan, as a variant of the letter C with a cedilla.